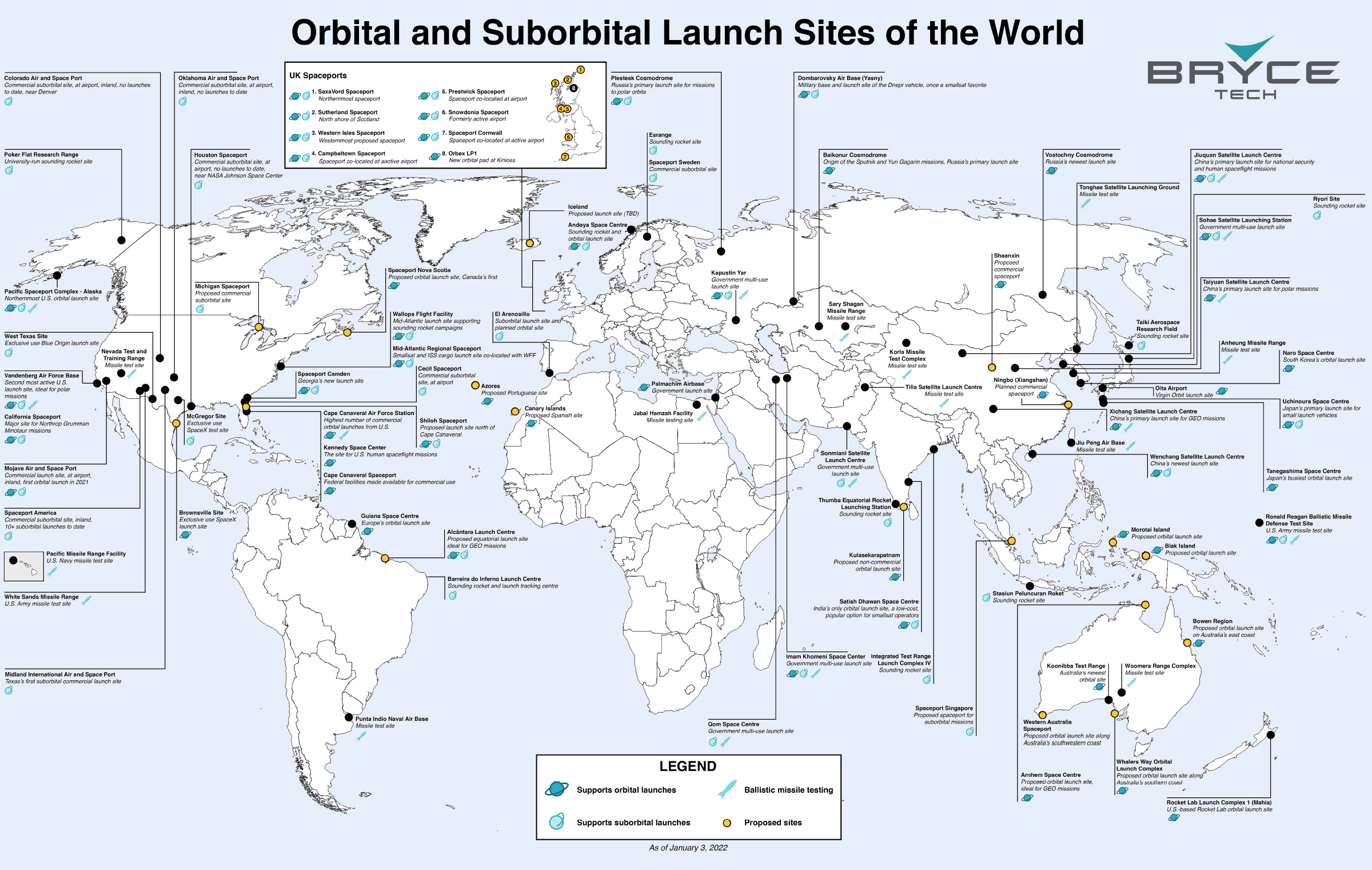
View the high-resolution map
Mapped: The World’s Rocket Launch Sites
From Sputnik 1 to today’s massive satellite constellations, every object in space was launched from just a handful of locations.
The map above, from BryceTech, is a comprehensive look at the world’s spaceports (both orbital and sub-orbital) as well as ballistic missile test sites.
The World’s Major Spaceports
Though the graphic above is a detailed list of many types of rocket launch sites, we’ll focus on major sites that are sending satellites and passengers into sub-orbit, orbit, and beyond.
Editor’s note: The above table includes all sites that are operational, as well as under construction, as of publishing date.
The list above covers fixed locations, and does not include SpaceX’s autonomous spaceport drone ships. There are currently three active drone ships—one based near Los Angeles, and the other two based at Port Canaveral, Florida.
Two of the most famous launch sites on the list are the Baikonur Cosmodrome (Kazakhstan) and Cape Canaveral (United States). The former was constructed as the base of operations for the Soviet space program and was the launch point for Earth’s first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1. The latter was NASA’s primary base of operations and the first lunar-landing flight was launched from there in 1969.
The global roster of spaceports has grown immensely since Baikonur and Cape Canaveral were the only game in town. Now numerous countries have the ability to launch satellites, and many more are getting in on the action.
Wenchang Space Launch Site, on the island of Hainan, is China’s newest launch location. The site recorded its first successful launch in 2016.
Location, Location
One interesting quirk of the map above is the lack of spaceports in Europe. Europe’s ambitions for space are actually launched from the Guiana Space Centre in South America. Europe’s Spaceport has been operating in French Guiana since 1968.
Low altitude launch locations near the equator are the most desirable, as far less energy is required to take a spacecraft from surface level to an equatorial, geostationary orbit.
Islands and coastal areas are also common locations for launch sites. Since the open waters aren’t inhabited, there is minimal risk of harm from debris in the event of a launch failure.
As demand for satellites and space exploration grows, the number of launch locations will continue to grow as well.